By: Anjali Mehta Chandar, Charlie Waller Institute, School of Psychology and Clinical Language Sciences (SPCLS), a.m.chandar@reading.ac.uk

Overview
Our vocational postgraduate courses in Low Intensity Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Children and Young People include a mix of face to face, and remote teaching on Blackboard, at an almost 50/50 split since the COVID-19 pandemic. It is important that trainees engage well with digital methods of learning, and a carousel technique was adapted for Blackboard Collaborate, with hugely positive feedback from the trainees.
Objectives
My objectives for this project were as follows:
- adapt the carousel activity from face to face teaching to remote teaching,
- gain feedback from trainees about the effectiveness of this strategy and,
- make changes as necessary for future implement with other cohorts.
Context
The Educational Mental Health Practitioner (EMHP) programme is a one-year vocational postgraduate course. The trainees are employed by an NHS trust, local authority or charity, and study in the Charlie Waller Institute (within SPCLS) to become qualified mental health practitioners working in primary and secondary schools.
Since the pandemic, trainees have half of their teaching face to face on campus, and half of it via Blackboard Collaborate. Teaching days are 9:30-4:30pm. It has been important, and a learning curve, to ensure online teaching remains as engaging as face to face teaching. It is suggested that a lack of engagement with digitally enhanced learning leads to students being academically disadvantaged (Francis & Shannon, 2013). It is also important that group work is still utilised despite a larger amount of remote teaching than before, as it is an effective method for fostering wider knowledge, clarification on a topic and evaluation of peers’ ideas (Hassanien, 2006).
Carousel activities are an engaging teaching method, and are commonly used in face to face teaching. With this technique, trainees work in small groups to complete an assigned task. Half of the trainees then stay with their projects to explain them, whilst the other half circulate around the room to hear about the other projects. The trainees then switch around, enabling everyone to have a chance to present to their peers, and hear about all the other projects and outcomes too. It was therefore important to try to emulate this for online teaching, as it was a well-received method in face to face teaching.
Implementation
I designed the teaching activity to be 30 minutes of small group work in breakout rooms, and then wanted some trainees to be able to move themselves to three different breakout groups (one every 5 minutes), before moving back to their own original group. Meanwhile the other half would stay in their own group for the first 15 minutes, explaining to their peers about their project ideas, before then moving around 3 groups for the last 15 minutes.
I was able to research how to adapt settings on Blackboard Collaborate to allow this to happen. By clicking ‘allow attendees to switch groups’ when setting up breakout rooms, trainees can move themselves.
Trainees were given strict instructions about the task, including what their project was about based on what group number they were, how to make notes of their project for presenting to their peers after, and how/when to switch groups to hear about other’s ideas. See slides below, which are also available for download as a PowerPoint file:




I was then able to use the chat function to let everyone know to move to the next group (every 5 minutes).
I then closed all breakout rooms after all switches had been made, and we discussed the projects as a whole class.
Impact
Shortly after the carousel task was completed, trainees completed their usual feedback for the teaching day using Menti.
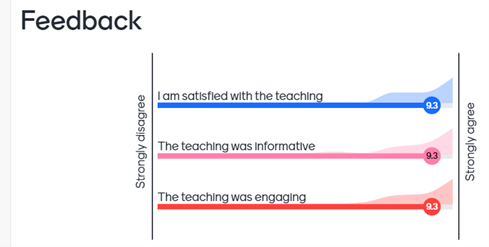
Below is the quantitative feedback about how satisfying, informative and engaging, the day was: (Note: this included other teaching techniques for three quarters of the day, and not just the carousel task in the final quarter.)
I was also able to see qualitative comments about the carousel task in particular, and noted how so many of the comments were specifically about this task. See below:
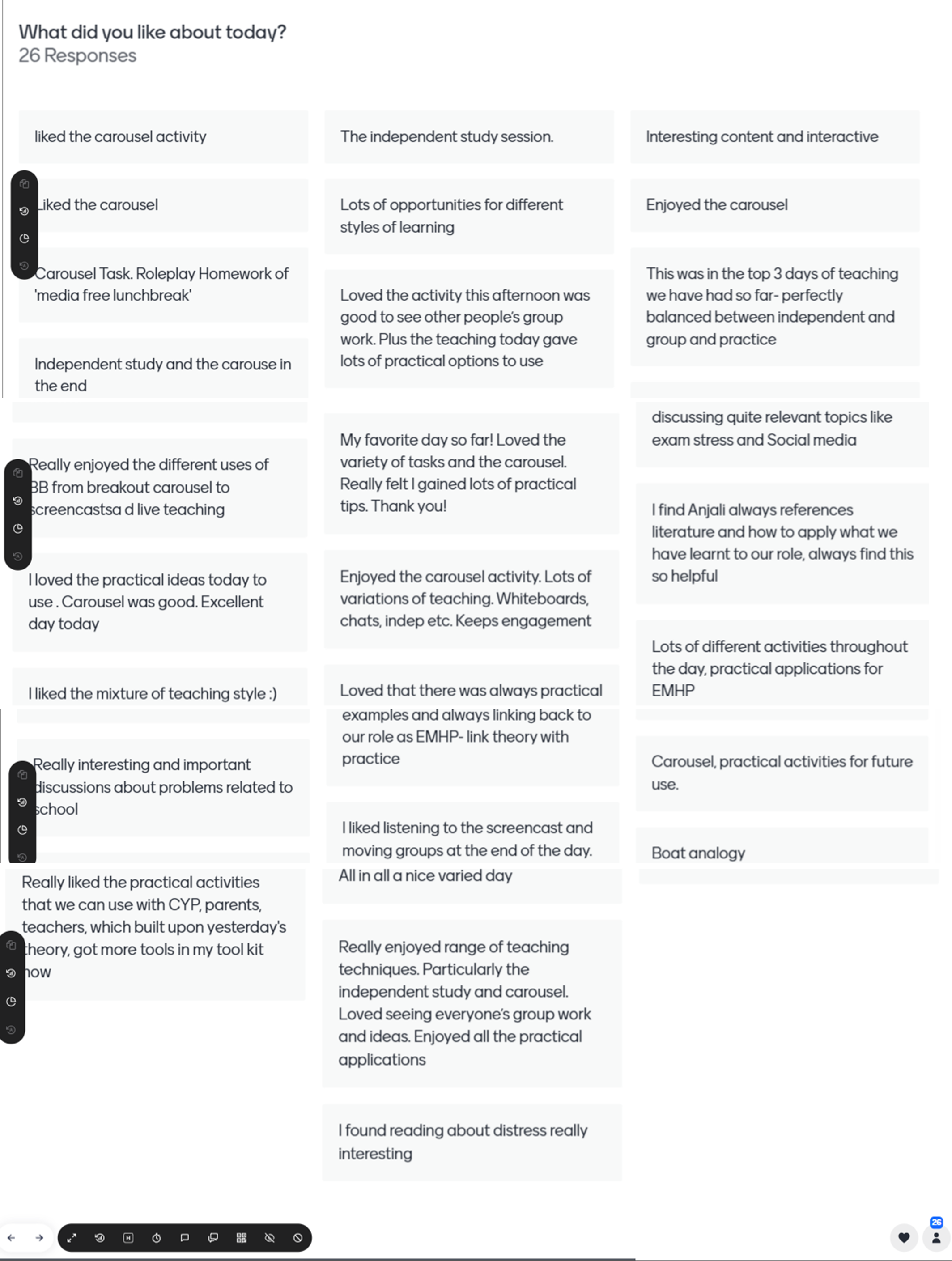
It seems that trainees appreciated the real-life aspect of the group task, which is in line with research by O’Neill and Short (2023) who found that ”real-world relevant” group tasks in higher education tend to engage students more.
There were only three pieces of feedback about the carousel activity when trainees were asked what could be improved in the day:
- “Carousel was a bit chaotic but enjoyed it more than I expected”
- “The carousel was not so much fun”
- “Felt rushed creating poster and then needing to share”
Whilst the first two are hard to make adjustments for as it is unclear what was not fun and what was chaotic, the third point can be solved by allowing more time for the task itself. However, I am also mindful that the majority of trainees completing the feedback did not state that this felt rushed. To balance this, I can check with trainees on the day if 30 minutes feels like enough time, and go with a majority vote for timing.
Overall, this activity was therefore able to meet its first two objectives:
- adapt the carousel activity from face to face teaching to remote teaching, and
- gain feedback from trainees about the effectiveness of this strategy.
The third objective was “to make changes as necessary for future implementation with other cohorts.” This has yet to be carried out due to the fact this teaching day resumed to face to face teaching the following year, but a similar technique can be utilised for other teaching days and content.
Reflections
Overall, I feel that the carousel technique was well implemented and only minor changes need to be taken forward. Specifically, this is about ensuring all trainees feel they have enough time for the initial project creation element.
From the feedback, I think trainees enjoyed the task. Clear instructions made this task work well, and trainees enjoyed being able to move themselves around breakout groups. This was perhaps more novel than usual, which may have sparked interest. Similarly, Meng et al. (2019) found that novel techniques in the pharmacy field led to improved learning and communication abilities, and improved academic performance.
Furthermore, the creativity was acknowledged in another section of the Menti feedback –“this was night and day compared to some of the other less creatively organised sessions” – which is in line with research about the importance of creativity in successful and effective teaching in higher education (Bidabadi et al., 2016).
Follow up
Since this teaching, I have noticed how it has not been implemented with other teaching days. For my upcoming allocated teaching, I have mapped out remote teaching days where I can implement this strategy again.
I plan to use the same format for structuring the activities and slides, with the added element of elicited feedback from trainees before the task about whether they feel they have enough time to complete it. I could also enter the different breakout groups and check that they feel they have finished.
I also hope that by disseminating this technique more widely and in more detail than previously – I shared it in the Charlie Waller Institute Teaching and Learning Significant Interest Group – more lecturers will feel able to implement this strategy and gain feedback on future changes to make.
References
Bidabadi, N. S., Isfahani, A. N., Rouhollahi, A., & Khalili, R. (2016). Effective teaching methods in higher education: requirements and barriers. Journal of Advances in Medical Education & Professionalism, 4(4), 170-178.
Francis, R., & Shannon, S. J. (2013). Engaging with blended learning to improve students’ learning outcomes. European Journal of Engineering Education, 38(4), 359-369.
Hassanien, A. (2006). Student experience of group work and group assessment in higher education. Journal of Teaching in Travel & Tourism, 6(1), 17-39.
Meng, X., Yang, L., Sun, H., Du, X., Yang, B., & Guo, H. (2019). Using a novel student-centered teaching method to improve pharmacy student learning. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 83(2), 171-179.
O’Neill, G., & Short, A. (2023). Relevant, practical and connected to the real world: what higher education students say engages them in the curriculum. Irish Educational Studies, 1-18.