Rita Balestrini and Elisabeth Koenigshofer, School of Literature and Languages, r.balestrini@reading; e.koenigshofer@reading.ac.uk
Overview
Working in collaboration with two Final Year students, we designed two ‘flexible’, ‘minimalist’ rubric templates usable and adaptable across different languages and levels, to provide a basis for the creation of level specific, and potentially task specific, marking schemes where sub-dimensions can be added to the main dimensions. The two marking templates are being piloted this year in the DLC. The project will feature in this year’s TEF submission.
Objectives
Design, in partnership with two students, rubric templates for the evaluation and feedback of writing tasks and oral presentations in foreign languages which:
- were adaptable across languages and levels of proficiency
- provided a more inclusive and engaging form of feedback
- responded to the analysis of student focus group discussions carried out for a previous TLDF-funded project
Context
As a follow-up to a teacher-learner collaborative appraisal of rubrics used in MLES, now DLC, we designed two marking templates in partnership with two Final Year students, who had participated in the focus groups from a previous project and were employed through Campus Jobs. ‘Acknowledgement of effort’, ‘encouragement’, ‘use of non-evaluative language’, ‘need for and, at the same time, distrust of, objective marking’ were recurrent themes that had emerged from the analysis of the focus group discussions and clearly appeared to cause anxiety for students.
Implementation
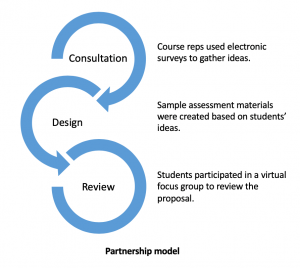
We organised a preliminary session to discuss these findings with the two student partners. We suggested some articles about ‘complexity theory’ as applied to second language learning, (Kramsch, 2012; Larsen-Freeman, 2012; 2015a; 2015b; 2017) with the aim of making our theoretical perspective explicit and transparent to them. A second meeting was devoted to planning collaboratively the structure of two marking schemes for writing and presentations. The two students worked independently to produce examples of standard descriptors which avoided the use of evaluative language and emphasised achievement rather than shortcomings. At a third meeting they presented and discussed their proposals with us. At the last meetings, we continued working to finalise the templates and the two visual learning charts they had suggested. Finally, the two students wrote a blog post to recount their experience of this collaborative work.
The two students appreciated our theoretical approach, felt that it was in tune with their own point of view and that it could support the enhancement of the assessment and marking process. They also found resources on their own, which they shared with us – including rubrics from other universities. They made valuable suggestions, gave us feedback on our ideas and helped us to find alternative terms when we were struggling to avoid the use of non-evaluative language for our descriptors. They also suggested making use of some visual elements in the marking and feedback schemes in order to increase immediateness and effectiveness.
Impact
The two marking templates are being piloted this year in the DLC. They were presented to colleagues over four sessions during which the ideas behind their design were explained and discussed. Further internal meetings are planned. These conversations, already begun with the previous TLDF-funded project on assessment and feedback, are contributing to the development of a shared discourse on assessment, which is informed by research and scholarship. The two templates have been designed in partnership with students to ensure accessibility and engagement with the assessment and feedback process. This is regarded as an outstanding practice in the ‘Assessment and feedback benchmarking tool’ produced by the National Union of Students and is likely to feature positively in this year’s TEF submission.
Reflections
Rubrics have become mainstream, especially within certain university subjects like Foreign Languages. They have been introduced to ensure accountability and transparency in marking practices, but they have also created new problems of their own by promoting a false sense of objectivity in marking and grading. The openness and unpredictability of complex performance in foreign languages and of the dynamic language learning process itself are not adequately reflected in the detailed descriptors of the marking and feedback schemes commonly used for the objective numerical evaluation of performance-based assessment in foreign languages. As emerged from the analysis of focus group discussions conducted in the department in 2017, the lack of understanding and engagement with the feedback provided by this type of rubrics can generate frustration in students. Working in partnership with them, rather than simply listening to their voices or seeing them as evaluators of their own experience, helped us to design minimalist and flexible marking templates, which make use of sensible and sensitive language, introduce visual elements to increase immediateness and effectiveness, leave a considerable amount of space for assessors to comment on different aspects of an individual performance and provide ‘feeding forward’ feedback. This type of ‘partnership’ can be challenging because it requires remaining open to unexpected outcomes. Whether it can bring about real change depends on how its outcomes are going to interact with the educational ecosystems in which it is embedded.
Follow up
The next stage of the project will involve colleagues in the DLC who will be using the two templates to contribute to the creation of a ‘bank’ of descriptors by sharing the ones they will develop to tailor the templates for specific stages of language development, language objectives, language tasks, or dimensions of student performance. We also intend to encourage colleagues teaching culture modules to consider using the basic structure of the templates to start designing marking schemes for the assessment of student performance in their modules.
Links
An account written by the two students partners involved in the project can be found here:
Working in partnership with our lecturers to redesign language marking schemes
The first stages of this ongoing project to enhance the process of assessing writing and speaking skills in the Department of Languages and Cultures (DLC, previously MLES) are described in the following blog entries:
National Union of Students 2017. The ‘Assessment and feedback benchmarking tool’ is available at:
http://tsep.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Assessment-and-feedback-benchmarking-tool.pdf
References
Bloxham, S. 2013. Building ‘standard’ frameworks. The role of guidance and feedback in supporting the achievement of learners. In S. Merry et al. (eds.) 2013. Reconceptualising feedback in Higher Education. Abingdon: Routledge.
Bloxham, S. and Boyd, P. 2007. Developing effective assessment in Higher Education. A practical guide. Maidenhead: McGraw-Hill International.
Bloxham, S., Boyd, P. and Orr, S. 2011. Mark my words: the role of assessment criteria in UK higher education grading practices. Studies in Higher Education 36 (6): 655-670.
Bloxham, S., den-Outer, B., Hudson J. and Price M. 2016. Let’s stop the pretence of consistent marking: exploring the multiple limitations of assessment criteria. Assessment in Higher Education 41 (3): 466-481.
Brooks, V. 2012. Marking as judgement. Research Papers in Education. 27 (1): 63-80.
Gottlieb, D. and Moroye, C. M. 2016. The perceptive imperative: Connoisseurship and the temptation of rubrics. Journal of Curriculum and Pedagogy 13 (2): 104-120.
HEA 2012. A Marked Improvement. Transforming assessment in HE. York: The Higher Education Academy.
Healey, M., Flint, A. and Harrington K. 2014. Engagement through partnership: students as partners in learning and teaching in higher education. York: The Higher Education Academy.
Kramsch, C. 2012. Why is everyone so excited about complexity theory in applied linguistics? Mélanges 33: 9-24.
Larsen-Freeman, D. 2012. The emancipation of the language learner. Studies in Second Language Learning and Teaching. 2(3): 297-309.
Larsen-Freeman, D. 2015a. Saying what we mean: Making a case for ‘language acquisition’ to become ‘language development’. Language Teaching 48 (4): 491-505.
Larsen-Freeman, L. 2015b. Complexity Theory. In VanPatten, B. and Williams, J. (eds.) 2015. Theories in Second Language Acquisition. An Introduction. New York: Routledge: 227-244.
Larsen-Freeman, D. 2017. Just learning. Language Teaching 50 (3): 425-437.
Merry, S., Price, M., Carless, D. and Taras, M. (eds.) 2013. Reconceptualising feedback in Higher Education. Abingdon: Routledge.
O’Donovan, B., Price, M. and Rust, C. 2004. Know what I mean? Enhancing student understanding of assessment standards and criteria. Teaching in Higher Education 9 (3): 325-335.
Price, M. 2005. Assessment standards: the role of communities of practice and the scholarship of assessment. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education 30 (3): 215-230.
Sadler, D. R. 2009. Indeterminacy in the use of preset criteria for assessment and grading. Assessment and evaluation in Higher Education 34 (2): 159-179.
Sadler, D. R. 2013. The futility of attempting to codify academic achievement standards. Higher Education 67 (3): 273-288.
Torrance, H. 2007. Assessment as learning? How the use of explicit learning objectives, assessment criteria and feedback in post-secondary education and training can come to dominate learning. Assessment in Education 14 (3): 281-294.
VanPatten & J. Williams (Eds.) 2015. Theories in Second Language Acquisition, 2nd edition. Routledge: 227-244.
Yorke, M. 2011. Summative assessment dealing. Dealing with the ‘Measurement Fallacy’. Studies in Higher Education 36 (3): 251-273.