Zainab Abdulsattar (student – Research Assistant), Tamara Wiehe (staff – PWP Clinical Educator) and Dr Allán Laville, a.laville@reading.ac.uk, (Dean for D&I and Lecturer in Clinical Psychology). School of Psychology and CLS.
Overview
To help Part 3 MSci Applied Psychology students address the emotional aspect of engaging with and interpreting assessment feedback, we have created a Blackboard feedback tool, which draws on self-help strategies used in NHS Mental Health services. This was a TLDF funded project by CQSD and we reflect upon the usefulness of the tool in terms of helping students manage their assessment feedback in a more positive and productive way for both now and the future.
Objectives
- To explore the barriers to interpreting and implementing feedback through the creation of a feedback-focused tool for Blackboard
- To transfer aspects of NHS self-help strategies to the tool
- To acknowledge the emotional aspect of addressing assessment feedback in Higher Education
- To support students to engage effectively with feedback
Context
Assessment and feedback are continually rated as the lowest item on student surveys despite efforts from staff to address this. Whilst staff can certainly continue to improve on their practices surrounding providing feedback, our efforts turned to how we could improve student engagement in this area. Upon investigation of existing feedback-focused tools, it has become apparent that many do not acknowledge the emotional aspect of addressing assessment feedback. For example, the ‘Development Engagement with Feedback Toolkit (DEFT)’ has useful components like a glossary helping students with academic jargon, but it does not provide resources to help with feedback related stress. The aim was to address the emotional aspect of interpreting feedback in the form of a self-help tool.
Implementation
Zainab Abdulsattar’s experience:
Firstly, we carried out a literature review on feedback in higher education and the use of self-help resources like cognitive restructuring within the NHS used to treat anxiety and depression. These ideas were taken to the student focus group: to gather students’ thoughts and opinions on what type of resource they would like to help them understand and use their feedback.

Considering ideas from the literature review and the focus group, we established the various components of the tool: purpose of feedback video, problem solving and cognitive restructuring techniques, reflective log and where to go for further support page. Then, we started the creation of our prototype Blackboard tool. At tool creation stage, we worked collaboratively with the TEL team (Maria, Matt and Jacqueline) to help format and launch the tool. Upon launch, students were given access to the tool via Blackboard and a survey to complete once they had explored and used the tool.
Impact
Our prototype Blackboard tool met the main objective of the project, to address the emotional aspect of the interpreting assessment feedback. The cognitive restructuring resource aimed to identify, challenge and re-balance students negative or stressful thoughts related to receiving feedback. Some students reported in the tool survey that they found this technique useful.
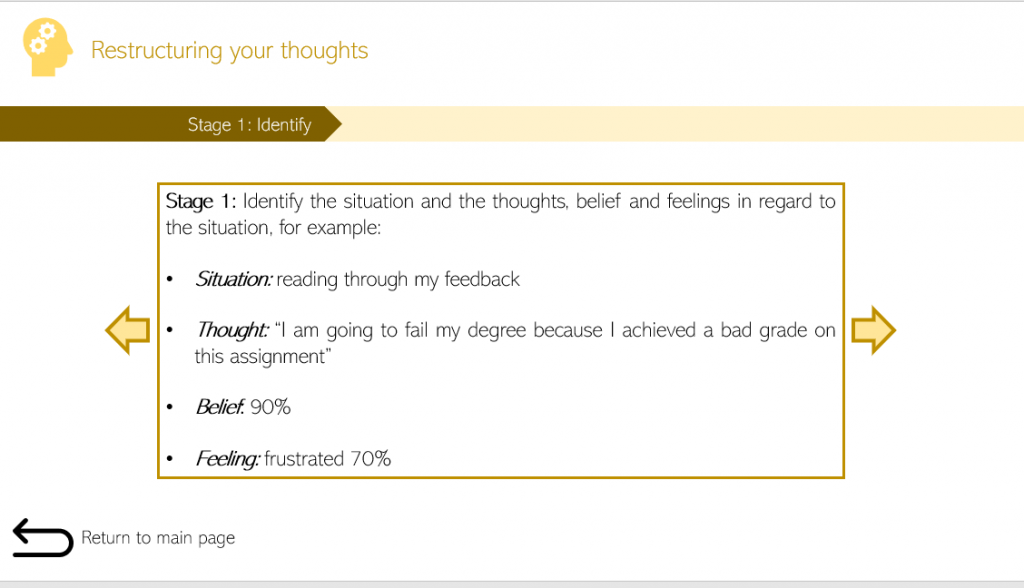
As well as this, the examples seemed to help students link their past experiences of not getting a good grade. Students also appreciated the interactive features like the video of the lecturer [addressing the fact that feedback is not a personal attack] and were looking forward to the tool being fully implemented during their next academic year. Overall, the student survey was positive with the addition of some suggestions such as making the tool smart phone friendly and altering the structure of the main page for ease of use.
Reflections
Zainab Abdulsattar’s reflections:
The success of the tool lied in the focus group and literature review contributions because the students’ focus group tool ideas helped to further contribute to the evidence-based self-help ideas gathered from the latter. Importantly, the hope is that the tool can act as an academic aid promoting and improving students’ independence in self-managing feedback in a more positive and productive way. Hopefully this will alleviate feedback-related stress for both now and the future in academic and work settings.
Follow up
In the future, we hope to expand the prototype tool into a more established feedback-focused tool. To make the tool even more use-friendly, we could consider improving the initial main contents page. For example, presenting the options like ‘I want to work on improving x’ then lead on to the appropriate self-help resource instead of simply starting with the resource options [e.g. problem solving, reflective log].