By: Rita Balestrini, Department of Languages and Cultures, r.balestrini@reading.ac.uk
Overview
The project built on T&L innovation embraced in the Department of Languages and Cultures (DLC), where Microsoft’s OneNote Class Notebook (CN) was trialled during the Covid-19 pandemic to overcome the constraints of teaching languages remotely. The outcomes provided knowledge of DLC students’ experience of CN and understanding of the type of support needed by CN users to staff users of CN, and to colleagues in Technology Enhanced Learning (TEL) and Digital Technology Services (DTS), and informed the development of technical and pedagogical support and guidance for CN users.
Objectives
The project aimed to enhance student learning by improving the use of CN, and had the objective to facilitate sharing of knowledge and expertise, gain insights into students’ experience of CN and inform TEL and DTS decision-making on the tool.
Context
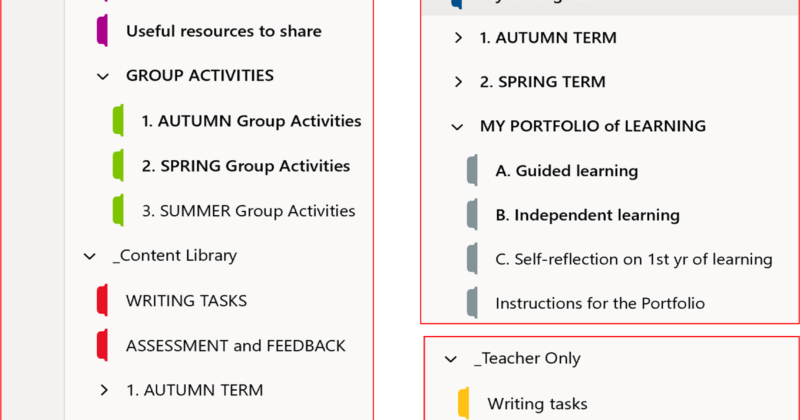
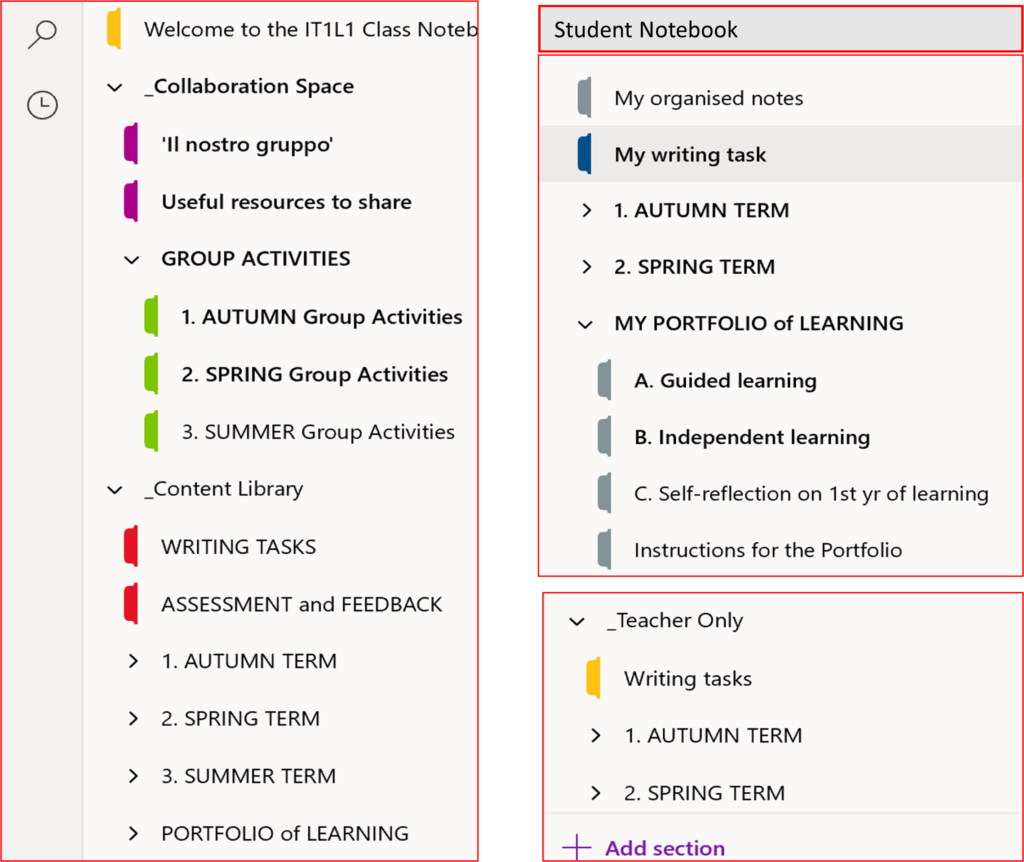
CN is a digital T&L tool to store materials (e.g. text, images, handwritten notes, links, recorded voice, videos), where students and teachers can work interactively in and outside the classroom. It is organised into three parts:
- ‘Content Library’ – where only the teacher can add, edit, and delete materials.
- ‘Collaboration Space’ – a place to collaborate in groups open to everyone in the class, where multiple users can work on a page simultaneously or asynchronously.
- ‘Teacher Only’ – a private space invisible to students.
- ‘Student Notebook’ – a private area that only a student and their teacher can see and use, where they can interact directly on a page.
CN continues to be used in some language modules as it proved to be effective beyond a remote teaching environment and offered features that supported accessibility and inclusivity in language learning.
Implementation
- In 2022–2023, I held three sessions with DLC staff users to share practice and ideas on using CN, and record information on what support would enhance teaching with CN. I also held in-person, small group meetings with DLC CN student users from all year groups to gain insights into their experience of CN. The feedback gathered informed the development of a branched MS Forms survey, which was completed by 28 (of 50) student CN users.
- I facilitated a cross-School (DLC, Institute of Education, Law) ‘teaching conversation’ to reflect critically on the pedagogical value of CN.
- I wrote a project report for DTS and TEL and shared with them the findings from the needs analysis.
Impact
- The project created a ‘space’ for the sharing of practices, knowledge, experience and expertise, which in turn, enabled the enhancement of the use of CN.
- It enhanced students’ learning and increased their engagement with CN learning activities – as evidenced by the students’ survey.
- As part of ‘internal monitoring and review’ practice, the outcomes of the ‘teaching conversation’, informed the School of Literature and Languages (SLL) T&L enhancement process.
- The project should inform the integration of CN with other applications (e.g. Teams), and the provision of technical and pedagogical support for CN users.
Reflections
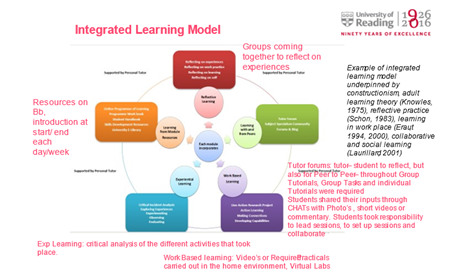
CN offers a paperless learning environment and facilitates the organisation of T&L materials in a clear and, ‘potentially’ visually intuitive, hierarchical structure. Students evaluated CN positively as a useful ‘digital binder’ and ‘learning tool’ (Average Rating [AR] 4.15 and 4:00 respectively, on a scale of 1 to 5). Most of them felt that materials and resources were easy to access (AR 3.89), and it was easy to take notes within CN (AR 3.74).
CN users generally agreed that navigation in CN is quite ‘fluid’ compared to Blackboard. However, I think that for this fluidity to be fully meaningful pedagogically CN requires a thoroughly thought-out structure, with reasoned and transparent ‘labelling’ throughout the learning environment.
There can be issues in meeting current assessment policies when using CN for summative assessment. However, CN greatly facilitates the provision of feedback with a digital pen or by audio-recording on a page. Staff value the possibility of monitoring individual and group activities and providing private, individualised feedback in different formats; students appreciate highly receiving feedback directly in their personal notebook, which stands out as a noteworthy result of the survey (AR 4.26), especially considering that feedback in general ‘is often framed as the dimension of students’ experience with which they are least satisfied’ (Winstone & Carless, 2020, p. 5).
The ‘Collaboration Space’ can be used for class activities, collaborative projects, sharing resources, and a channel for students’ voice – additional uses of this area depend on the subject taught. CN allows students to take ownership of a shared area and use it for independently chosen purposes, which helps create a sense of ‘community’ and a feeling of ‘online connectedness’ (Hehir et al., 2021).
Regarding technical issues, 68% of respondents did not report any. The others mentioned a variety of problems (e.g. syncing issues, ‘handwriting’ and ‘highlighting’ not anchored to text). Many reported difficulties were linked to using different CN versions, devices, or operating systems, which suggests that improvements could come with advice from technical support specialists.
Follow up
In future, students’ experience of using CN could greatly benefit from:
- staff sharing and discussing practices across different subjects to facilitate pedagogical enhancements (e.g., communities of practice, special interest groups, TEL forums);
- making access to CN easier and facilitating its integration with Teams and Blackboard;
- the availability of expert support from DTS and TEL (e.g. technical assistance, TEL resources and sessions for users).
References
- Hehir, H., Zeller M., Luckhurst, J., & Chandler T. (2021) Developing student connectedness under remote learning using digital resources: a systematic review. Education and Information Technologies, 26, 6531-6548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10577-1
- Winstone, N., & Carless, D. (2020) Designing effective feedback processes in higher education. Routledge.