Kat Hall, School of Chemistry, Food and Pharmacy, k.a.hall@reading.ac.uk
Overview
The Centre for Inter-Professional Postgraduate Education and Training (CIPPET) provide PGT training for healthcare professionals through a flexible Masters programme built around blended learning modules alongside workplace-based learning and assessment. This project aimed to evolve the department’s approach to delivering one of our clinical skills workshops which sits within a larger 60 credit module. The impact was shown via positive student and staff feedback, as well as interest to develop a standalone module for continuing further learning in advanced clinical skills.
Objectives
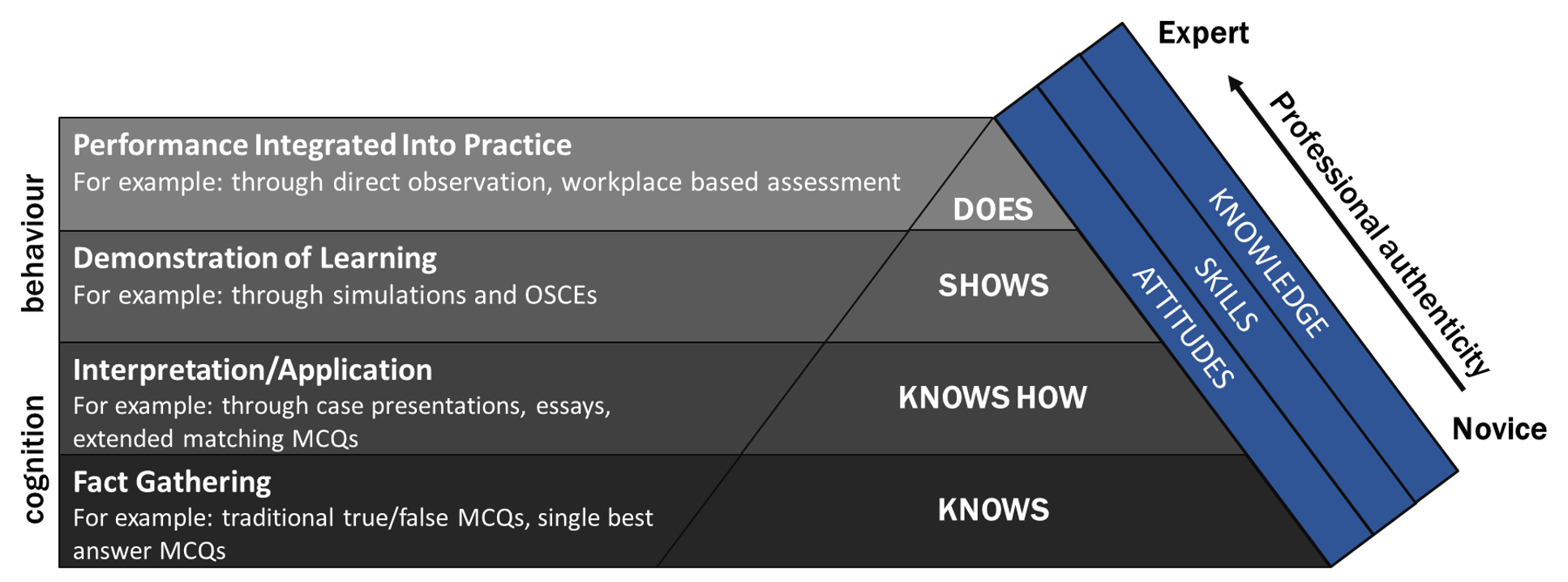
The aim of this project was to use controlled condition assessment approaches to develop behavioural competence at the higher levels of Miller’s pyramid of clinical competence 1.
Miller’s Pyramid of Clinical Competence
The objectives included:
- engage students in enquiry by promoting competence at higher levels of Miller’s pyramid
- develop highly employable graduates by identifying appropriate skills to teach
- evolve the workshop design by using innovative methods
- recruit expert clinical practitioners to support academic staff
Context
Health Education England are promoting a national strategy to increase the clinical skills training provided to pharmacists, therefore this project aimed to evolve the department’s approach to delivering this workshop. The current module design contained a workshop on clinical skills, but it was loosely designed as a large group exercise which was delivered slightly differently for each cohort. This prevented students from fully embedding their learning through opportunities to practise skills in alongside controlled formative assessment.
Implementation
Equipment purchase: As part of this project matched funding was received from the School to support the purchase of simulation equipment which meant a range a clinical skills teaching tools could be utilised in the workshops. This step was undertaking collaboratively with the physician associate programme to share learning and support meeting objective 2 across the School.
Workshop design: the workshops were redesigned by the module convenor, Sue Slade, to focus on specific aspects of clinical skills that small groups could focus on with a facilitator. The facilitators were supported to embed the clinical skills equipment within the activities therefore promoting students in active learning activities. The equipment allowed students the opportunity to simulate the skills test to identify if they could demonstrate competence at the Knows How and Shows How level of Miller’s Pyramid of Clinical Competence. Where possible the workshop stations were facilitated by practising clinical practitioners. This step was focused on meeting objectives 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Workbook design: a workbook was produced that students could use to identify core clinical skills they required in their scope of practice and thus needed to practise in the workshop and further in their workplace-based learning. This scaffolding supported their transition to the Does level of Miller’s Pyramid of Clinical Competence. This step was focused on meeting objectives 1 and 3.
Impact
All four objectives were met and have since been mapped to the principles of Curriculum Framework to provide evidence of their impact.
Mastery of the discipline / discipline based / contextual: this project has supported the academic team to redesign the workshop around the evolving baseline core knowledge and skills required of students. Doing this collaboratively between programme teams ensures it is fit for purpose.
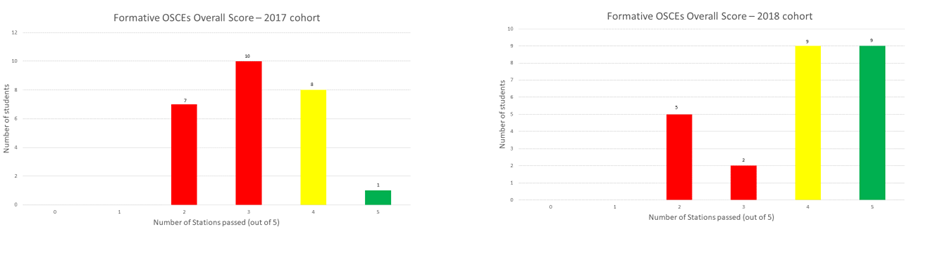
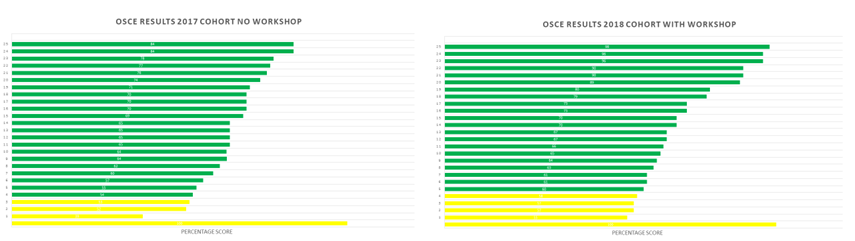
Personal effectiveness and self-awareness / diverse and inclusive: the positive staff and student feedback received reflects that the workshop provides a better environment for student learning, enabling them to reflect on their experiences and take their learning back to their workplace more easily.
Learning cycle: the student feedback has shown that they want more of this type of training and so the team have designed a new stand-alone module to facilitate extending the impact of increasingly advanced clinical skills training to a wider student cohort.
Reflections
What went well? The purchase of the equipment and redesigning the workshop was a relatively simple task for an engaged team, and low effort for the potential return in improved experience. By having one lead for the workshop, whilst another wrote the workbook and purchased the equipment, this ensured that staff across the team could contribute as change champions. Recruitment for an advanced nurse practitioner to support the team more broadly was completed quickly and provided support and guidance across the year.
What did not go as well? Whilst the purchase of the equipment and workshop redesign was relatively simple, encouraging clinical practitioners to engage with the workshop proved much harder. We were unable to recruit consistent clinical support which made it harder to fully embed the project aims in a routine approach to teaching the workshop. We considered using the expertise of the physician associate programme team but, as anticipated, timetabling made it impossible to coordinate the staffing needs.
Reflections: The success of the project lay in having the School engaged in supporting the objectives and the programme team invested in improving the workshop. Focusing this project on a small part of the module meant it remained achievable to complete one cycle of change to deliver initial positive outcomes whilst planning for the following cycles of change needed to fully embed the objectives into routine practice.
Follow up
In planning the next series of workshops, we plan to draw more widely on the University alumni from the physician associate programme to continue the collaborative approach and attract clinical practitioners more willing to support us who are less constrained by timetables and clinical activities.
Based on student and staff feedback there is clearly a desire for more teaching and learning of this approach and being able to launch a new standalone module in 2020 is a successful output of this project.
Links and References
Miller, G.E. (1990). The assessment of clinical skills/competence/performance. Acad Med, 65(9):S63-7.